Economics Of Distillation
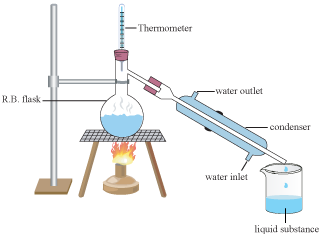







Economics Of Distillation
One of the ways a distiller can help offset some of the increased costs of therapeutic distillation is through the marketing of hydrosols. If the waters are not cohobated, distillation produces a lot of hydrosol - hundreds of litres, actually. Although not every drop produced throughout the distillation run is of therapeutic value, somewhere between twenty and thirty percent of the output can be used from an average large still.
Although each litre only sells for a few dollars, every twenty litres per run times the multiples f runs can amount to a reasonable sum of money added to the value of the essential oils. The distillers I work with have told me that selling their hydrosols has made a positive difference in their yearly incomes, and they consider hydrosols a coproduct, not a by-product, of the distillation process.
Essential oils produced by therapeutic distillation are expensive: are extremely labour intensive to produce: require the eye, hand, and heart of an artist combined with the mind of a scientist: and do not produce huge profits for the producers.
However, they not only offer us healing properties but can help us commune with and access the actual "life force" and knowledge of the plant, and on a larger scale they connect us with the planet and each other in new and healing ways. Spending more to purchase these oils is an easy choice when you look at it like this.
Reference: Hydrosols The Next Aromatherapy : Suzanne Catty
Articles - Most Read
- Home
- What are Hydrosols
- What are Hydrosols-2
- The Monographs
- How to Make a Hydrosol
- Distilled or Extracted Specifically For Therapeutic Use - 3
- Table of Common Latin Names and pH Values - F - O
- Kurt Schnaubelt
- What isn't a Hydrosol?
- Table of Common Latin Names and pH Values - P - S
- Wholly Water!
- Blue Babies
- Supply and Demands
- Mature Skin
- Recipes Alpha F
- Hydrosols In The Marketplace
- Nelly GrosJean
- Hemorrhoids
- Chemicals: Friends or Foes?
- Water as Medicine
- Influences
- The Educated Consumer
- Genitically Modified Plants
- Water Quality
Articles-latest
- Daucus carota/Wild Carrot Seed - pH 3.8-4.0
- Cupressus sempervirens/ Cypress-pH3.5-3.7
- Coriandrum sativum/Coriander Herb-and-Seed
- Comptonia peregrinal/Sweet Fern- pH 3.8
- Citrus clementine (fe) Clementine Petitgrain- pH 4.3-4.4
- Citrus aurantium var. amara (flos) /Neroli Orange Blossom-pH3.8-4.5
- Cistus ladaniferus/Rock Rose-pH 2.9-3.1
- Cinnamomum zeylanicum (ec) Cinnamon Bark-pH3.3
- Chamaemelum nobile/Roman Chamomile - pH 3.0-3,3
- Centaurea cyanus/Cornflower/Bachelor's Button-pH 4.7-5.0
- Cedrus atlantical/Cedarwood/Atlas Cedar-pH 4.1- 4.2
- Hydrosols -The PH - Anomalies
- Hydrosols- Establishing Shelf Life and Stability
- Boswellia carterii/FRANKINCENSE
- Asarum canadense/ Wild Ginger/Canadian Ginger
- Artemesia vulgaris / Artemesia
- ARTEMESIA DRACUNCULUS - TARRAGON
- Angelica archangelica / Angelica Root - Hydrosols
- The Key, or More Correctly, the pH - 2 - Hydrosols
- The Key, or More Correctly, the pH-Hydrosols
- The Hard pHacts - Hydrosols
- Calamus Root/Sweet Flag - ACORUS CALAMUS
- Yarrow - Achillea millefolium - Hydrosols
- Balsam Fir - Abies balsamea - Hydrosols